An emerging trend in SEO is the growing adoption of structured data on websites, especially with the introduction of AI and Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) impacting on search results. As such, SEO Specialists have begun to leverage structured data in order to make their websites stand out on Google.
Schema is an important part of Technical SEO, yet it is often under-utilised compared to more common practices synonymous with the industry, such as Copywriting and Link Building. While it does not directly boost search rankings, it helps search engines understand the context of page content, leading to better indexing. This can result in more accurate and visually appealing displays in search results (like rich snippets, knowledge graphs, etc.), leading to potentially better engagement.
While it may seem like we are using structured data and schema interchangeably, there are distinctions to note before going forward. Data structure generally refers to how data is organised on a website, including how it’s linked and presented. This can involve website architecture, navigation, and internal linking. “Schema,” on the other hand, specifically refers to a set of vocabularies (Schema.org) used to implement structured data on websites. Schema helps define the type of content present on a webpage (like articles, products, reviews) in a way that’s understandable to search engines. Essentially, schema is a specific avenue of structuring data to communicate with search engines more effectively.
At Ambire, we’re striving to demystify all things related to structured data and its relation to schema so you can propel your website’s SEO in 2024.
What Is Schema Markup?
Schema is a data-structure vocabulary that defines entities, actions, and relationships across the internet – think web pages and emails. This vocabulary makes it possible for search engines to understand the meaning behind subject matter across the web, and in turn provides a better user experience for everyone.
As Google continues to bring forth new updates that pushes towards building a Semantic Web, implementing schema markup becomes increasingly valuable for effective internet communication. As a result of adding schema tags to your website, Google and other search engines can enhance your listings on results pages by featuring additional information relevant to your content. This is presented through the form of rich snippets, which have a proven track record for boosting organic click-through-rate (CTR).
Rich Snippets and The Different Types of Schema Markups
Microdata rich snippets are commonly also referred to as rich results or enhanced search results. As mentioned, they provide additional information and visual elements to listings on SERPs. These are designed to help users better understand the content of a page prior to clicking through. They overall provide a more informative and engaging search experience.
Whether you’re an online publication, an e-commerce site, or a brick and mortar store looking to bolster your local SEO schema, your website listings can benefit from the inclusion of rich snippets. There is an ever growing catalogue of different schema markup types, which means there are likely
Google rich snippets relevant to your specific industry. Here are just a few of the most popular types of schema markup which you are bound to regularly stumble across when browsing the web.
There are different types of schema markups that you may require for your website. Here are some of the types:
Article Schema:
- Purpose: Used for news, blog posts, and articles.
- Function: Helps search engines understand article content, including the headline, author, and published date. It can enhance visibility in search results.
Breadcrumb Schema:
- Purpose: Used to mark up breadcrumb navigation on a site. Breadcrumb navigation refers to a feature that shows users their current location in the site’s hierarchy and provides links back to each previous page the user navigated through, usually found at the top of the page.
- Function: It helps search engines display the page’s position in the site hierarchy in search results, enhancing user understanding of where the page fits within the website.
Event Schema:
- Purpose: Used for events like concerts, webinars, or festivals.
- Function: Helps search engines understand event details such as date, location, and ticket availability. This can lead to richer search results, displaying key event information directly in the SERPs.
FAQ Page Schema:
- Purpose: Used on pages with a list of questions and answers on a specific topic to assist customers.
- Function: Allows search engines to display these questions and answers directly in search results, potentially increasing visibility and click-through rates. It’s particularly useful for voice search and Google Assistant answers.
How-To Schema:
- Purpose: Used for instructional content on a website.
- Function: Helps search engines understand the steps involved in a how-to guide. It can result in rich snippets in search results that display a part of the steps or a summary, improving visibility and enticing users.
These are just a few of the most common structured data types used to complement a website’s SEO. Feel free to browse through a full list of schema markup types you can use to define elements on your website.
Different Types Of Markup Formats
Before you go about trying to spruce up your organic search listings with rich snippets, it’s important to know that there are several types of commonly used markup formats which you may use to do so.
RDFa (Resource Description Framework in Attributes)
RDFa is an HTML extension that allows you to embed structured data within HTML tags using attributes. It provides a way to express semantic information about the content on a webpage. RDFa uses various attributes, such as “property,” “typeof,” and “resource,” to annotate HTML elements with structured data. This markup format helps search engines understand the meaning and relationships of the data on a webpage.
JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data)
JSON-LD is a JavaScript-friendly format for representing structured data. It provides a way to embed schema markup using JSON objects within script tags. JSON-LD separates the structured data from the HTML content, making it easier to add and maintain schema markup. It allows developers to associate a wider range of information with a web page and is often preferred due to its simplicity and flexibility. JSON-LD can be used in various contexts, including webpages, emails, and web APIs.
Microdata
Microdata is an HTML5 specification that allows you to embed structured data directly within HTML tags using specific attributes. It provides a straightforward way to add semantic annotations to HTML elements. Microdata uses attributes like “itemscope,” “itemtype,” and “itemprop” to define the structured data and its properties. It allows you to mark up various types of content, such as products, articles, events, and more. Microdata markup is supported by major search engines and is an effective way to implement schema markup.
How To Implement Schema On Your Website
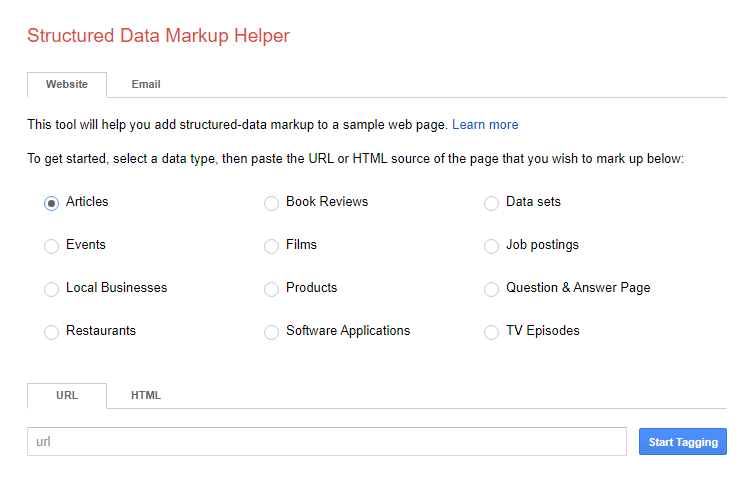
Google has introduced the Structured Data Markup Helper to simplify the process of adding the most common types of structured data to your website. The tool allows you to either submit URLs for existing landing pages, or even entire HTML blocks.
1. To start off, paste the URL or HTML of the page you wish to enhance with rich snippets and proceed to “Start Tagging”.
- We have used one of our latest blog posts as an example to demonstrate how the tool works. We will be using the schema markup for “Articles” in our walkthrough as this structured data type is most relevant to our blog post.
- Please note that the same steps mostly apply regardless to the types of schema markup you intend on implementing.
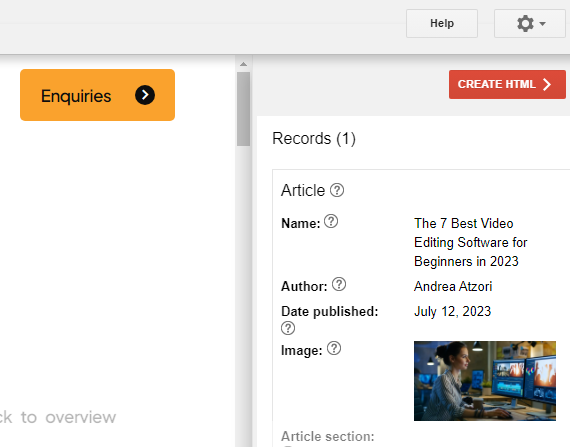
2. Assign tags to various elements across the page once it has loaded within the interactive tool.
- You can see that once we have highlighted our heading, we’re prompted to assign it with a tag.
- On the right hand side of the tab, you can find a checklist of common items you’re ideally going to want to cover. It’s not a dealbreaker if you can’t tick them all off, but it’s best practice to attend to as many as possible for your schema to be most effective.
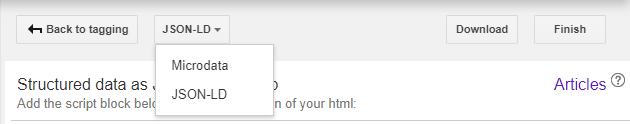
3. Once you’ve finished with tagging your page, proceed to click “Create HTML”.
- Google will now generate schema markups relevant to elements you have tagged on your page.
4. You will have the option to change the markup format between Microdata & JSON-LD. Google has expressed in its structured data guidelines that it recommends the use of JSON-LD over Microdata for schema implementation – though either is fine.
- The The implementing schema markup process will vary according to the format you wish to process with.
- For JSON-LD, you’ll simply be instructed to paste the code Google has generated for your page into the head section of its HTML.
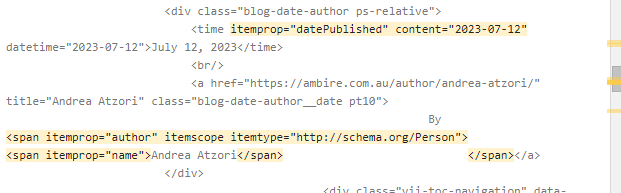
- Microdata will require you to manually insert specific lines of text throughout your HTML. Google’s tool will highlight the additional code that will need to be added in order to markup each relevant element.
Schema Plugins For Content Management Systems
Many popular content management systems (CMS) also allow for schema plugins which make it possible to mark up pages across your domain en masse. They often come with intuitive interfaces which are preferable for users who may not have the courage to mess with the code on their website.
One of the most effective WordPress schema plugins available on the market is Schema Pro. It’s highly intuitive to use, features more than 20 schema types, and has a feature enabling users to create templates which automate the markup process across multiple pages.
Another popular option is Yoast SEO. This is because most SEOers will probably already have the plugin installed on their WordPress sites. Though it’s important to note that Yoast’s primary function is not to implement schema. As such, it’s a little more complicated to use when compared to plugins which are dedicated to implementing schema markup.
If you’re looking for a free schema plugin for WordPress then you should check out All In One Schema Rich Snippets. The plugin is still actively supported by the developers and receives regular updates. With 60,000+ active installations and over 100 5 star reviews, this is arguably the most effective way to implement schema and structured data for wp sites for free.
Webmasters for e-commerce sites are more likely to be looking for Shopify schema plugins instead. Shopify actually has an app store which enables users to effortlessly browse through the best schema plugins available for the platform. Additionally, they have published a comprehensive guide on how users may manually add schema to a Shopify site.
How To Test Schema Once Implemented
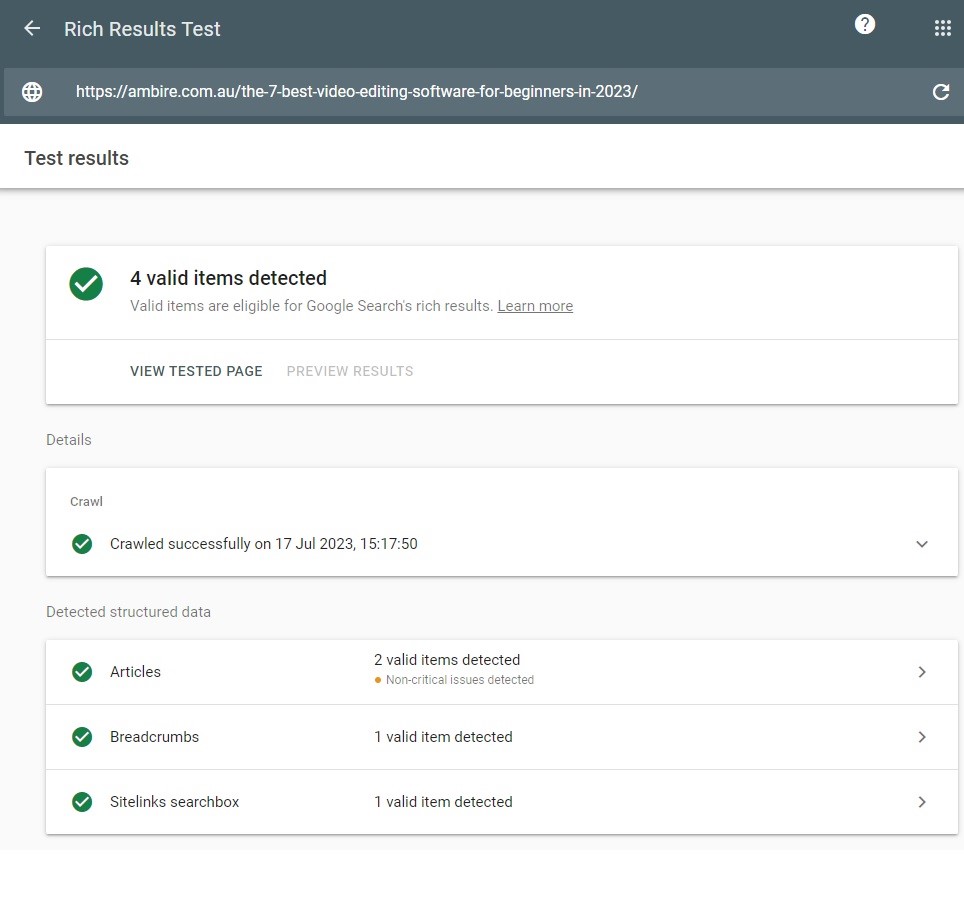
Once you have added schema to your site, you may be eager to test to see if it has been implemented correctly – especially if it’s your first time. Luckily, Google has another tool to help us check this. Simply input the URL or HTML code into the Rich Results Test and it will show you which rich snippets your page is eligible to display on SERPS.
We’ve gone ahead and updated our most recent blog post with the schema that Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper generated for us. After publishing these changes and submitting our blog into the Rich Results Test, it can be seen that the page in question now features the structured data required to generate rich snippets on Google.
Does Schema Have An Impact On SEO Rankings In 2024?
As mentioned previously, rich snippets have an unquestionable impact on CTR, but can the same be said for search rankings? Google representative and SEO wizard, John Mueller, has actually come out and announced that Structured Data is not a direct ranking factor. The operative word here being “direct”.
As discussed, structured data is simply a language model used to help search engines better understand the content of your website. It is this very context that also makes it intrinsically easier for search engines to appropriately rank your site. When implemented correctly, it may lead to improved keyword targeting and greater organic visibility for queries which are semantically related to your priority keywords.
Schema Markup In 2024 & Beyond
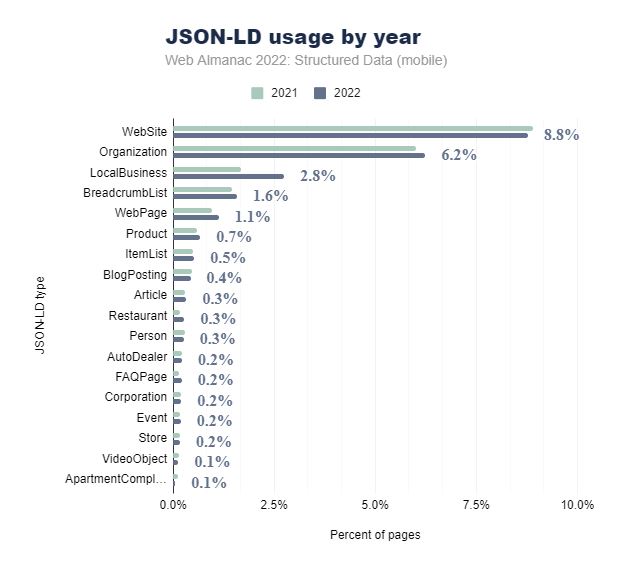
The HTTP Archive has conducted research pertaining to the implementation of structured data through the JSON-LD format in 2022. Their findings suggest that there were a greater number of mobile homepages which featured schema markup when compared to the previous year.
It is expected that this trend will persist throughout the following years, and this isn’t exclusively because Google rewards websites with rich snippets. As mentioned, schema is simply a data-structure vocabulary which aims to create an universal list of semantic tags which may be used to present data in a machine readable format.
This has recently become especially relevant with the increased interest surrounding artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP). Though schema.org doesn’t directly help with the development of NLP, it may prove to have a number of useful applications relevant to machine learning. For instance, developing an AI system which focuses on curating the news can rely on the NewsArticle schema type to pinpoint the most relevant content.
From an SEO perspective, it may also be crucial to start adding schema markup to your website as Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) looms over the horizon. SGE is Google’s attempt at integrating generative AI content into their search results – making it possible for users to effectively find content relevant to their hyper-specific queries.
Some marketers are concerned that these generative AI results may push their websites further down the SERPs and reduce their organic visibility. An even greater threat would be that users may have their curiosities satiated solely through generative AI content, thus reducing clicks onto actual websites.
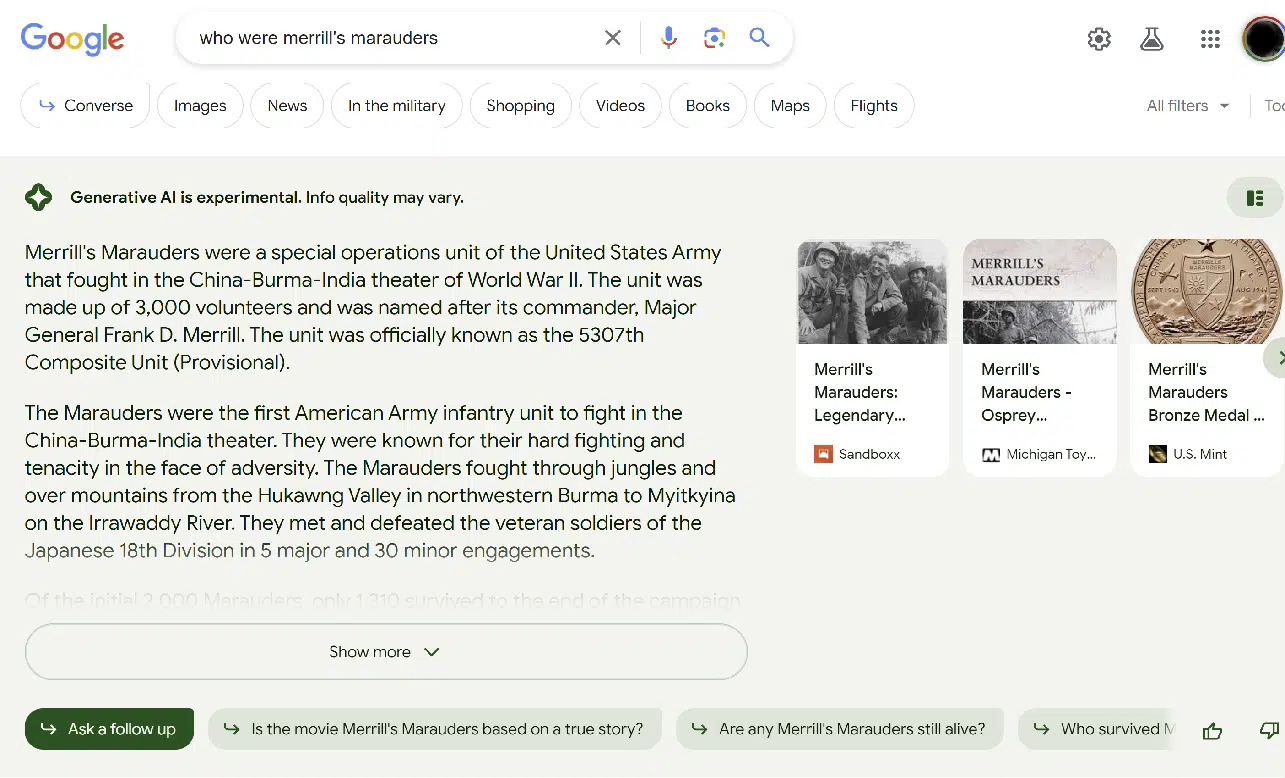
Though it’s not all gloom and doom. Remember that AI relies on human generated content to produce their results. This can be seen in the above example where sources used to draft generative AI results are cited. It’s reasonable to assume that helping search engines to better understand the content of your pages with structured data will increase the likelihood of your content being cited in generative search results.
As generative results are currently featured on the top of the page, being cited in this section can almost be likened to ranking for a featured snippet. As such, implementing schema markup on your website in 2024 is a sensible way to future-proof your website in the leadup to Google’s Search Generative Experience. Regardless of whether SGE ever takes off, adding schema to your site will also dramatically increase the likelihood of boosting your organic CTR through rich snippets.
Given Google’s history of striving towards a Semantic Web, it would be highly advisable to begin introducing schema markup to your website to ensure greater success in the evolving organic landscape.