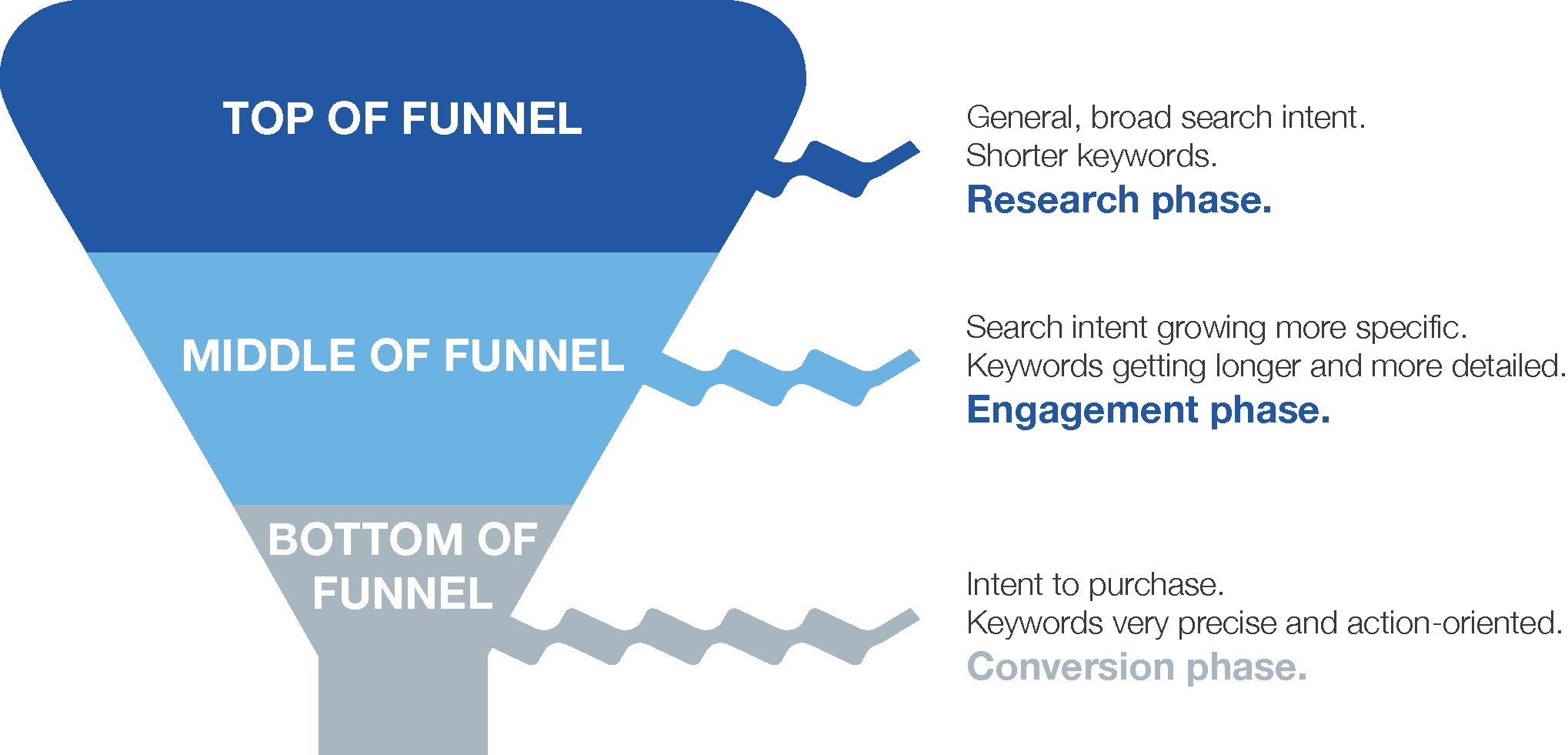
In the ‘good old days’ Twitter’s character limit was 140, so, in an ode to this, we’re keeping our definitions short in this SEO dictionary.
As I just did in that very, very brief introduction.
So, without further ado or character wastage – let’s dive into a helpful SEO glossary where we define common SEO terms in less than 140 characters each.
But, if you’re more interested in the 7 horrible SEO mistakes you might not realise you’re making? We’ve also got you covered.
SEO can get pretty technical.
THE SEO DICTIONARY
301 Redirect: A signal to search engines that a page has moved, users are taken to the closest matched page instead.
404 Error: A signal the web page could not be found, as it’s normally moved or deleted and no redirect set up.
Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP): Pages optimised for, and designed to load more quickly on, mobile devices.
Algorithms: How Google calculates search engine rankings, changing constantly to ensure the most relevant search result is returned for a user’s search.
Anchor text: Text which links you to other pages.
Authority: A measure of a website’s strength, built up over time via backlinks, stronger authority contributes to better search engine rankings.
Backlinks: Inbound links that come into your site from other websites, social media or directories, quality of these will determine site ranking.
Black-hat SEO: Practices designed to trick search engines into improving rankings and likely to be punished by Google for violating quality guidelines.
Bots: Also called spiders or crawlers, they check the readability of your site by following links.
Bounce rate: Percentage of visitors who leave your site having only viewed one page.
Broken links: Links which do not lead anywhere on your page or the web.
Cascading style sheets (CSS): These make websites look good or bad by controlling fonts, sizes, colours etc.
Citations: Listings which include a business’ name, address, opening hours and contact details like email or phone number, maps or directories.
Click-Through Rate (CTR): How many times your website is clicked when it shows up in a SERP, good CTRs improve organic search rankings as it shows the site is relevant.
Competition: How many other sites are using the same term and optimising for it. Beware of high competition phrases as they are too hard to rank for.
Conversion: When a visitor completes an action on your site, whether it’s purchasing or signing up to email.
Crawling: How search engines travel and index web pages.
Deep link: A link that takes users to pages deep within your site, usually on the blog.
Featured Snippets: A summary of an answer to a user’s query, displayed at the top of Google search results, extracted from site and includes title and URL.
Google Ads: Google’s advertising platform, wildly successful, ads sold on a cost-per-click basis.
Check out our handy guide for Google Ads in 2021 or learn more about our approach to Google Ads management.
Google Analytics: A free web analytics tool from Google which allows you to monitor your website’s performance.
Google My Business: Google’s tool for managing your Google Maps listing for your business.
H1 – H6: Heading tags which organise the page for the visitor and for Google, make the page easier to read for both.
HyperText Markup Language (HTML): The programming code used to create web pages.
Index: The database of content collected by search engine spiders, stored and organised as they crawl.
Intent: What users really mean or what they really want from their search query, e.g. ‘pizza’ – restaurants, takeaway, recipes, ingredients or nutritional information?
Internal Links: Links on your website which direct visitors to other pages within your website.
Keyword Density: How many times your keyword appears in your content, too high a density and content is unnatural and difficult to read, can incur a penalty.
Keyword research: The process of identifying which words, terms and phrases are being used when your audience searches your products and services.
Keywords: Search terms you’re trying to optimise for, long-tail are best as they are more specific, e.g. “wood-fired Pizza Sydney” over “pizza”.
Keyword stuffing: A black hat SEO technique where you put too many keywords on the page making it very difficult and strange to read.
Landing Page: The page on your website that serves as the first page a person will view, not always the home page if you’ve been directed by links.
Local Search: Needs to be optimised for if you’re a business with a physical location, usually begins with a Google Maps listing.
Learn more about Local SEO.
Meta Descriptions: The tag which is displayed in the SERPs just under the heading, best if it’s unique to page content.
Meta Directive: Code which is invisible to human visitors but shows bots how to read the page.
Organic Search: Listings displayed on Google, Yahoo, and Bing which are not paid for, unlike the ads which pop up above.
Page Speed: The amount of time it takes for a page to load, takes into account image size and mobile view.
Pay-Per-Click (PPC): An advertising model where the advertiser only pays when someone clicks on the ad, the most famous example is Google Ads.
Personalisation: A search engine’s ability to change the SERPs based on location and a user’s previous search queries.
Penalties: Incurred from Google by sites using black hat or short-cut SEO methods which result in poor user experience, takes the form of lost rankings.
Ranking: How well your website does online and how high it sits in SERPS, you want to be found high up on the first page to be doing well.
Relevancy: How relevant your content is to the search query, the higher this is, the more likely you are to show up on the first page.
Robots.txt: A file on your website telling the search engine crawlers where to avoid or not to go.
Search engine optimisation (SEO): Umm, search engine optimisation is, well, read the rest of this dictionary!
Or, see our SEO services page.
Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs): What pops up when you type in a search term or query into Google, page one is where all the action is.
Search volume: Number of searches done for a keyword over a period of time (normally a month).
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL): Makes your site appear as https instead of http, looks much more secure to visitors.
SEO consultant: An SEO expert whose job it is to ensure your website improves its SERP rankings and user experience.
We think some can even be cooler than Michael Jordan.
Site Speed: How quickly a sample group of your web pages load.
Structured Data: Code that gives search engines information about a page’s content, also how Google lists information like movie times or recipes on the SERP.
Traffic: Visits to your website.
Voice Search: Allows the user to use a voice command to search the Internet, a site, or an app.
White Hat SEO: “Good guy” SEO practices, those in line with Google’s quality requirements.
XML Sitemap: A file on your website that tells the search engines what to explore.
Zero-Click SERP: The answer to a search query is displayed directly at the top of a Google search result, no clicks required to satisfy the user.
SEO can seem confusing, we get it. But hopefully armed with this SEO dictionary, you’ve been able to simplify some of the more complex terms and concepts.
You can also check out our Social Media marketing glossary as well – also done in 140 characters per definition.
See what we do here at Ambire that can help make SEO work for you and your business goals.